

Potomania or psychogenic polydipsia affects 6% to 20% of psychiatric populations, especially affecting people with schizophrenia.
Gamze Erzin
Unlike the normal behavior of drinking water when you feel thirsty, people with potomania drink compulsively, without the sensation of thirst being the trigger.
It is interesting to know this alteration. And excessive consumption of water can lead to serious consequences for the body, we must drinking too much water can be bad for your heart and brain.
Health risks associated with potomania
According to Morcillo et al., when water intake exceeds the elimination capacity of the kidney, which is approximately 12 liters per day, a dangerous imbalance in the body’s electrolytes, known as hypotonic hyponatremia.
This imbalance can negatively affect almost all body systems, especially the neurological system, causing confusion, seizures and coma.
Furthermore, this alteration in the electrolyte balance can cause heart problems such as arrhythmias and, if left untreated, can be fatal.
Drinking too much water can be fatal as it affects organs such as the brain and heart.
According to Macías Robles, “Patients with psychiatric disorders can develop hyponatremia even with water intake less than the renal excretion capacity.””.
This is due to the increased vasopressin secretiona hormone influenced by the medications they take, the psychiatric pathology itself and even smoking.
Causes of potomania
The causes of potomania can be of psychological origin and organic origin.. Among the organic causes is damage to the hypothalamus (a part of the brain that regulates thirst) or alterations in antidiuretic hormone, and Mellitus diabetes.
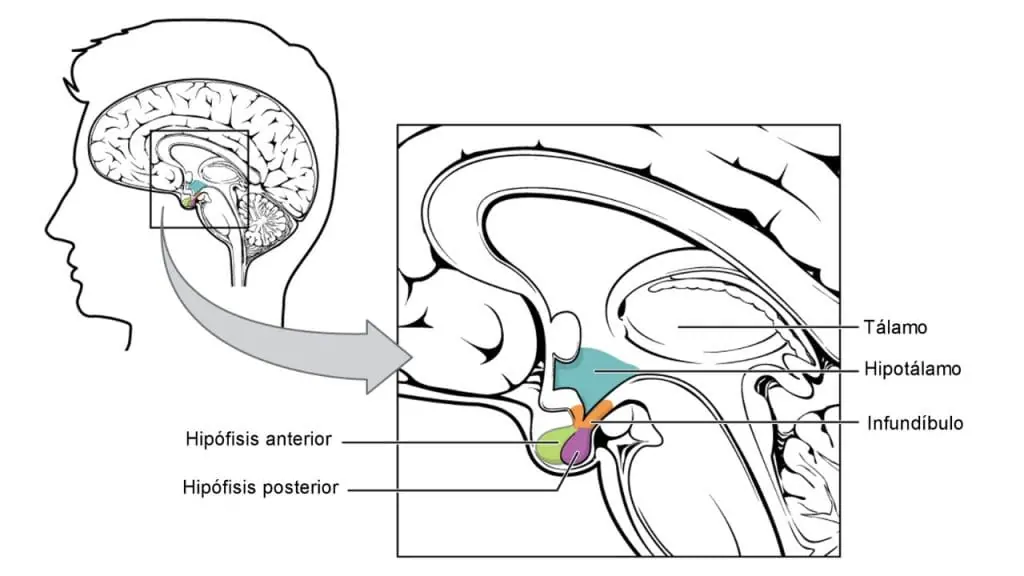
The antidiuretic hormone (ADH)also known as vasopressinis essential to regulate the elimination of water in the body.
This hormone is produced in the hypothalamus and is stored in the back of the hypophysis (also called pituitary gland), and its main function is to concentrate urine to reduce water loss.
If there is a ADH deficiencymay be due to damage to the pituitary or hypothalamus (due to a head injury, tumor, surgery, etc.) is known as central diabetes insipidus. And it is one of the organic causes that must be ruled out.
On the other hand, Psychological causes include psychotic disorders such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and dementia, including Alzheimer’s.
It is also observed in eating disorders as the anorexywhere a lot of liquid is consumed to feel full without calories, or to gain weight before a medical check-up.
Other disorders, such as vigorexia and orthorexiacan also lead to excessive fluid intake due to erroneous beliefs about its benefits.
Certain medications, such as some anti-inflammatories, diuretics, and lithium, can interfere with kidney function and contribute to this disorder..
Symptoms and diagnosis of potomania
The most common symptoms of potomania include a insatiable thirst despite drinking large amounts of fluid, the need to urinate frequently, even during the night, and bloating due to excess fluid, leading to edema.
Additionally, those affected may experience muscle cramps and fatigue constant due to the lack of balance in the electrolyte levels such as sodium and potassium. Also frequent are nausea, vomiting and stomach pain due to fluid saturation, as well as Headaches.
In more severe cases, potomania can cause drowsiness and, in extreme situations, body paralysis and Heart problems that can lead to congestive heart failure or death from arrhythmias.
The decrease in sodium in the blood, known as hyponatremiamay cause Hyponatremic encephalopathy, a condition that can result in stupor, seizures, coma, and even death.
The psychological symptoms of potomania are also significant. Affected people may experience changes in personality and behavior due to electrolyte imbalance.
Besides, the concentration reduction and loss of mental agility are common, since low sodium concentration affects brain function. The Aclinical anxiety and the panic attacks They can arise if the person cannot consume water for any reason. This constant need to drink water can make it difficult for the person to lead a normal life, as the desire to drink controls the person’s daily life.
For all these symptoms, the early detection and proper treatment of potomania They are essential to avoid fatal consequences. If you, or someone around you, has these symptoms, seek help from a health professional.

Available treatments
To apply the appropriate potomania treatmentFirst of all, it is important to take an individualized history. This has to take into account all the physical and psychological aspects of the patient.
As we have seen, some hormonal conditions, such as diabetes mellitus, can cause polydipsia (excessive thirst), so early diagnosis and proper management of these diseases is essential.
From a physical point of view, it is recommended minimize the use of medications that interfere with kidney function, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, thiazide diuretics, lithium, and anticholinergic medicationsas they can cause dry mouth.
Early management of hyponatremia is also important, so it is necessary to control and monitor the sodium levels in the blood.
He psychological treatment of potomania presents several challenges, as affected people often have a intense desire to drink watermaking it difficult for them to follow recommendations to reduce fluid intake.

In severe cases, it may even be necessary to limit the patient’s mobility to an area without access to water sources. That is to say, The main treatment for psychogenic polydipsia is controlled limitation of fluid intake under the supervision of a therapist..
Are used cognitive-behavioral techniques to help the patient control their anxiety and gradually reduce water intake. Some of these techniques include muscle relaxation, controlled breathing, and self-instructions to reduce anxiety.
In some cases, the system of Token Economy (a psychological behavior modification technique) to strengthen self-control, especially in people with schizophrenia.
Another important aspect of the treatment is cognitive restructuringwhich is useful for correcting erroneous beliefs about the benefits of drinking large amounts of water.
In serious cases, psychological treatment will be accompanied by Pharmacotherapy to try to avoid the organic consequences of excessive fluid intake.
In conclusion, potomania is a serious disorder normally associated with mental pathologies but it can also have an organic origin that must be ruled out. It can have fatal consequences if not treated properly.
It is essential to seek professional help if you suspect potomania. The goal is to avoid electrolyte imbalances that can be fatal, as well as other related health problems such as kidney, heart and neurological complications.
Bibliography
- Bhatia, M.S., Goyal, A., Saha, R., & Doval, N. (2017). Psychogenic polydipsia – management challenges. Shanghai Archives of Psychiatry, 29(3), 180. https://doi.org/10.11919/j.issn.1002-0829.216106
- Erzin, G., Ozdel, K., & Karadağ, H. (2017). Psychogenic polydipsia: A case report. European Psychiatry: The Journal of the Association of European Psychiatrists, 41(S1), S681–S682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpsy.2017.01.1181
- Martínez, SM, Ruiz, LA, Vicente, NH, Navarro, VD, Alegre, RH, & López, MG (2023, December 13). Potomania, an analysis of an atypical cause of severe hyponatremia in patients with severe mental disorder. Health Research Magazine. https://revistasanitariadeinvestigacion.com/potomania-un-analisis-sobre-una-causa-atipica-de-hiponatremia-grave-en-pacientes-con-trastorno-mental-grave/
- Moll, JU (2017, November 2). Potomania: symptoms, causes and treatment. Psychology and Mind Portal. https://psicologiaymente.com/clinica/potomania

